Solar Power (PV) System:


High-quality panels, internationally recognised for high output performance, deliver you more power for each watt installed. Individually quality tested and proven product that will stand up to the harshest Australian conditions.
Show less

Solahart checks flash test results for each panel and performs Electro-luminescence (EL) imaging on samples from each batch of panels to ensure there are no defects that will affect the performance of the PV system.
Show less

We provide a trusted Solahart Warranty on all our products, which means years of trouble-free, worry-free energy.
Show lessKey Features
Solar power panels need the sun’s light to generate electricity during the day, so it’s most economical to install a system that can supply your expected daytime electricity usage. Our smallest solar power system needs just 10 sqm of roof space to generate around 30% of the average Australian household’s energy use. The more power you want to generate, the bigger the roof space you need.
Our new high-performance Solahart SunCell panel is the ideal solution for Australian homes thanks to its innovative half-cell technology. 25-Year Solahart Product Warranty for peace of mind, plus, 30-Year Performance Guarantee for long term returns. Download Datasheet here.
The GoodWe inverter range is well suited for most rooftop installations. This rugged outdoor inverter has been designed as a completely sealed unit to withstand the harshest environmental conditions.
Our extensive network of Solahart Experts is qualified to assess your home and provide you with the best systems to meet your family’s needs. Our installers are trained to the highest standards to ensure the safety and effectiveness of your system. All this is backed by our comprehensive warranties and the peace of mind you’ll get from dealing with Australia’s solar pioneer.
- Trouble-Free - designed and engineered for Aussie conditions
- Latest 440W N-type Solahart SunCell panels
- Solahart SunCell 25 Year Australian Product Warranty
- Solahart SunCell 30 Year Performance Guarantee, at least 87.4% nominal power at 30 years
† Solahart Warranty Details:
- Solar Panels: 25 years,
- Inverter: 10 years,
- Racking and Balance of System components: 5 years,
- Labour: 5 years,
- For full warranty details, please visit the warranty page here.
Solahart Premium PV systems Specifications
Solahart SunCell Solar Panel Specifications
SOLAHART440R2
| Panel Electrical Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Maximum Power (Pmax) Power Class |
440Wp +/-5W |
| Open Circuit Voltage (Voc) | 38.80V |
| Short Circuit Current (Isc) | 14.3A |
| Maximum Power Voltage (Vmp) | 32.61V |
| Maximum Power Current (Imp) | 13.49A |
| Module Efficiency (%) | ≥22.5% |
| Normal Module Operating Temperature (NMOT) | 41±2°C |
| Temperature Coefficients | |
| PMPP VOC ISC |
-0.35%/°C -0.25%/°C +0.043%/°C |
| Maximum System Voltage ( IEC ) | 1500V |
| Maximum Reverse Current | 25A |
| Panel Specifications | |
| Dimensions | 1722 mm x 1134 mm x 30 mm |
| Weight | 21.3 kg |
| Cell Type and configuration | 6 x 18 monocrystalline solar half-cells |
| Back sheet | White |
| Frame | Black Anodised Aluminium |
| Junction Box | Protection Class IP 68 with bypass diodes |
| Connectors | MC4 EVO2A Connectors (PV-KST4 EVO 2A & PV-KBT4 EVO 2A) |
| Part Number | Solahart440R2 |
| Solahart Warranty | 25 Years Product Warranty* |
Solar Inverter Specifications
Inverter specification details can be found by downloading the inverter data sheet. Download
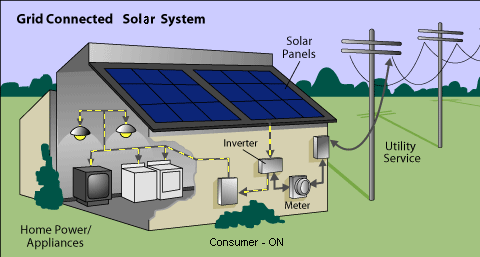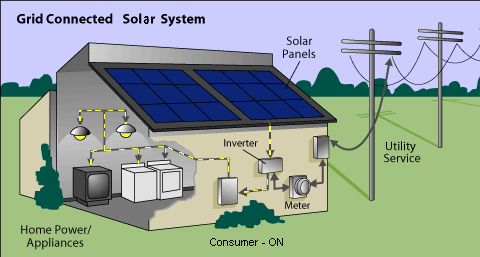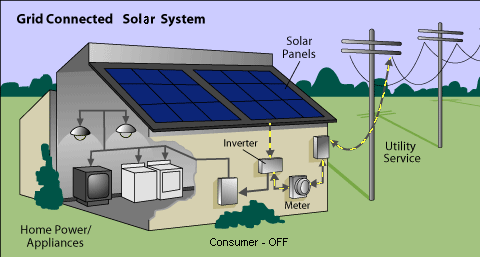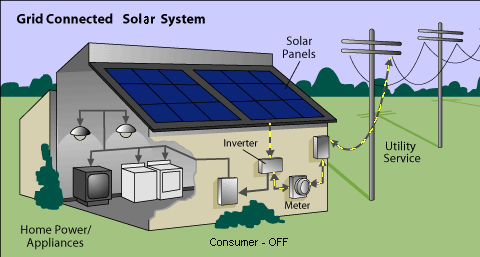
How Solar Power (PV) Systems Work
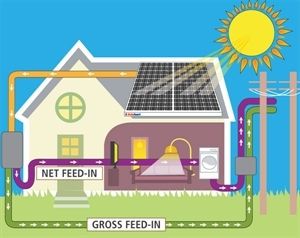
Solar power panels generate electricity from sunlight. The roof-mounted solar panels are made up of many photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells collect the sun’s light and convert the energy into DC electricity. This is fed through an inverter and converted to 240V AC electricity to power your home.
The amount of electricity you can produce depends on the number and efficiency of the panels, the size of the inverter and the amount of sunlight in your location. Your home remains connected to the electricity grid, so when you generate more electricity than you need, you can feed it into the grid or purchase more from the grid when you are not producing enough to meet your requirements.
The Science Explained
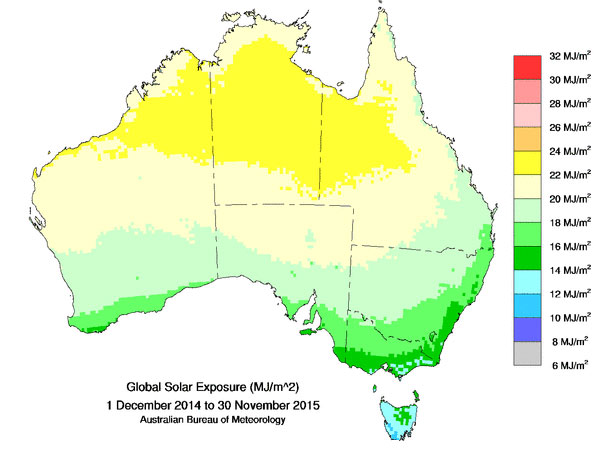
The amount of energy from the sun that falls on Earth's surface is enormous. All the energy stored in Earth's coal, oil, and natural gas reserves is matched by the energy from just 20 days of sunshine. Outside Earth's atmosphere, the sun's energy contains about 1,300 watts per square meter. About one-third of this light is reflected back into space, and some is absorbed by the atmosphere (in part causing winds to blow).
By the time it reaches Earth's surface, the energy in sunlight has fallen to about 1,000 watts per square meter at noon on a cloudless day. Averaged over the entire surface of the planet, 24 hours per day for a year, each square meter collects the approximate energy equivalent of almost a barrel of oil or 4.2 kilowatt-hours of energy every day. Deserts, with very dry air and little cloud cover, receive the most sun—more than six kilowatt-hours per day per square meter
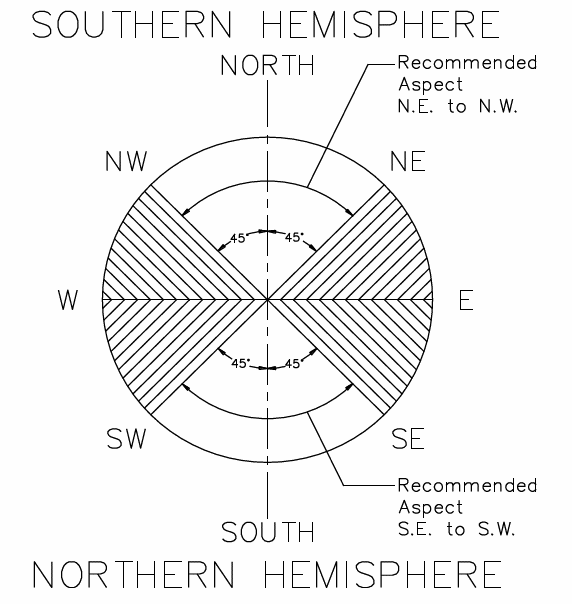
PV Panel Orientation & Inclination
To maximise system output, install panels at optimum orientation and inclination (tilt) angles. The specifics of this will depend on the installation location and must be calculated by a qualified system designer. The ideal angle for mounting a panel should result in the sun’s rays falling perpendicular (i.e. at a 90° angle) to the panel surface.
Panels should be installed in a shade-free position. Even minor or partial shading of the panels/array will reduce system output. A panel is considered shade free when it is both:
- Free from shade or shadows all year round.
- Exposed to several hours of direct sunlight, even during the shortest days.